🧠 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) helps doctors make better diagnoses, scientists create new materials, farmers grow crops more effectively and all of us driving cars - and millions of other applications. This topic also covers subsets of AI such as machine learning (ML), deep learning and neural networks.
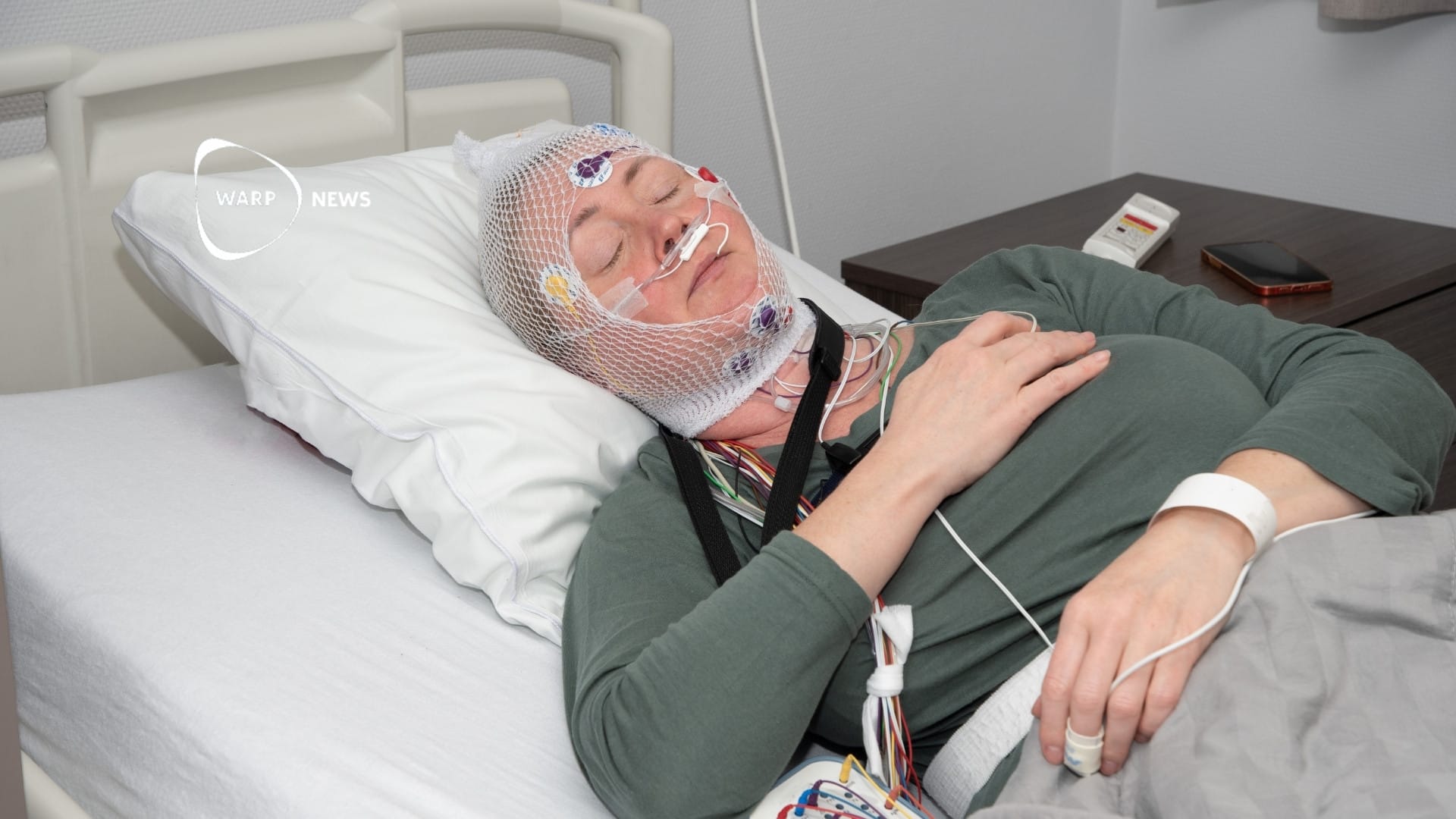
😴 New AI model can predict over 100 diseases from one night's sleep
The model was trained on nearly 600,000 hours of sleep data from 65,000 participants and shows high accuracy for cancer, heart disease, and dementia, among others. The AI model performs as well as or better than today's leading methods for sleep analysis.
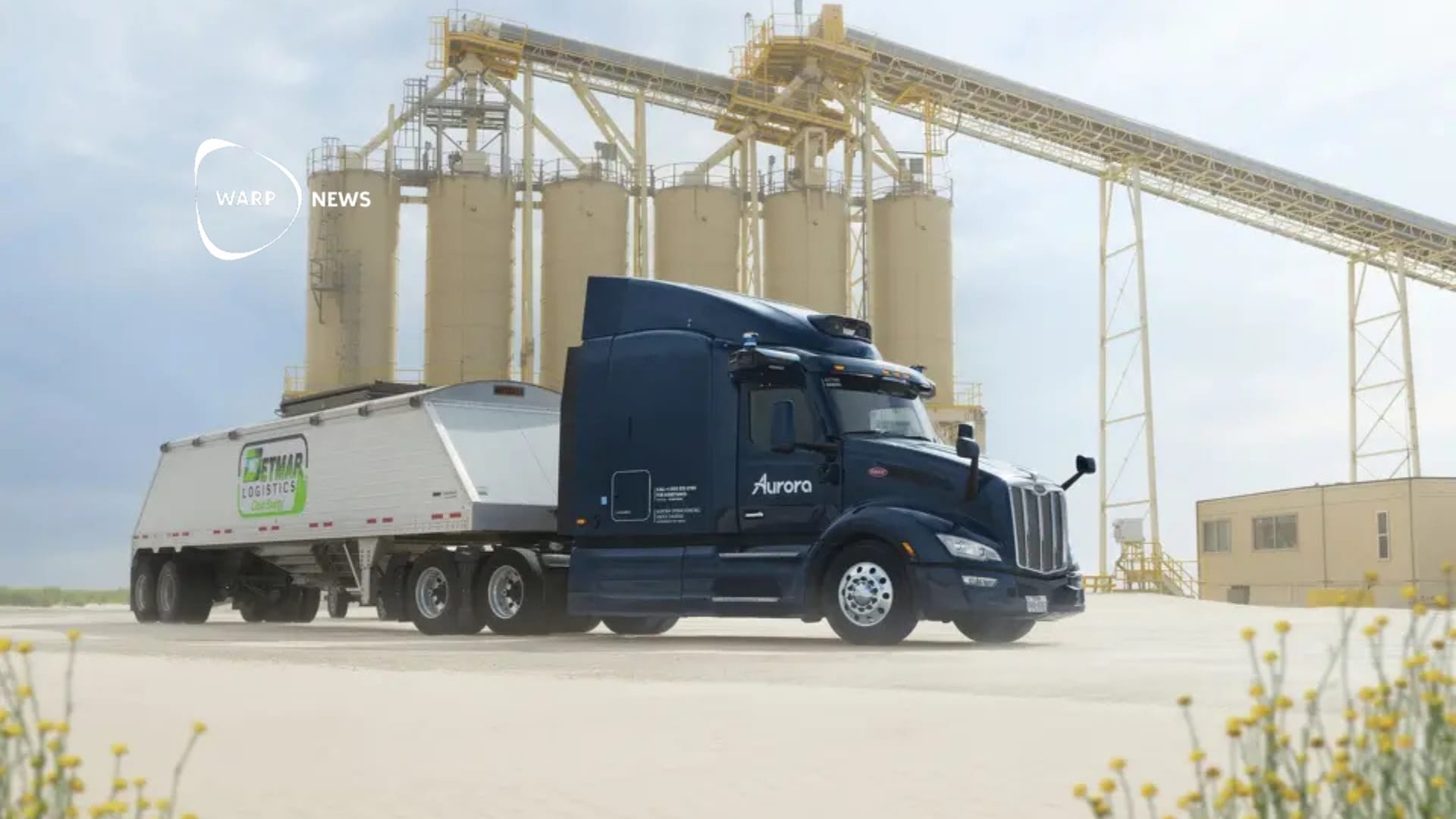
🚛 Self-driving trucks to transport sand around the clock in Texas
Detmar Logistics has signed an agreement with Aurora Innovation to use autonomous trucks to transport frac sand in the Permian Basin. The trucks can operate over 20 hours per day and double the capacity to move sand. The technology allows the vehicles to see 400 meters ahead in total darkness.
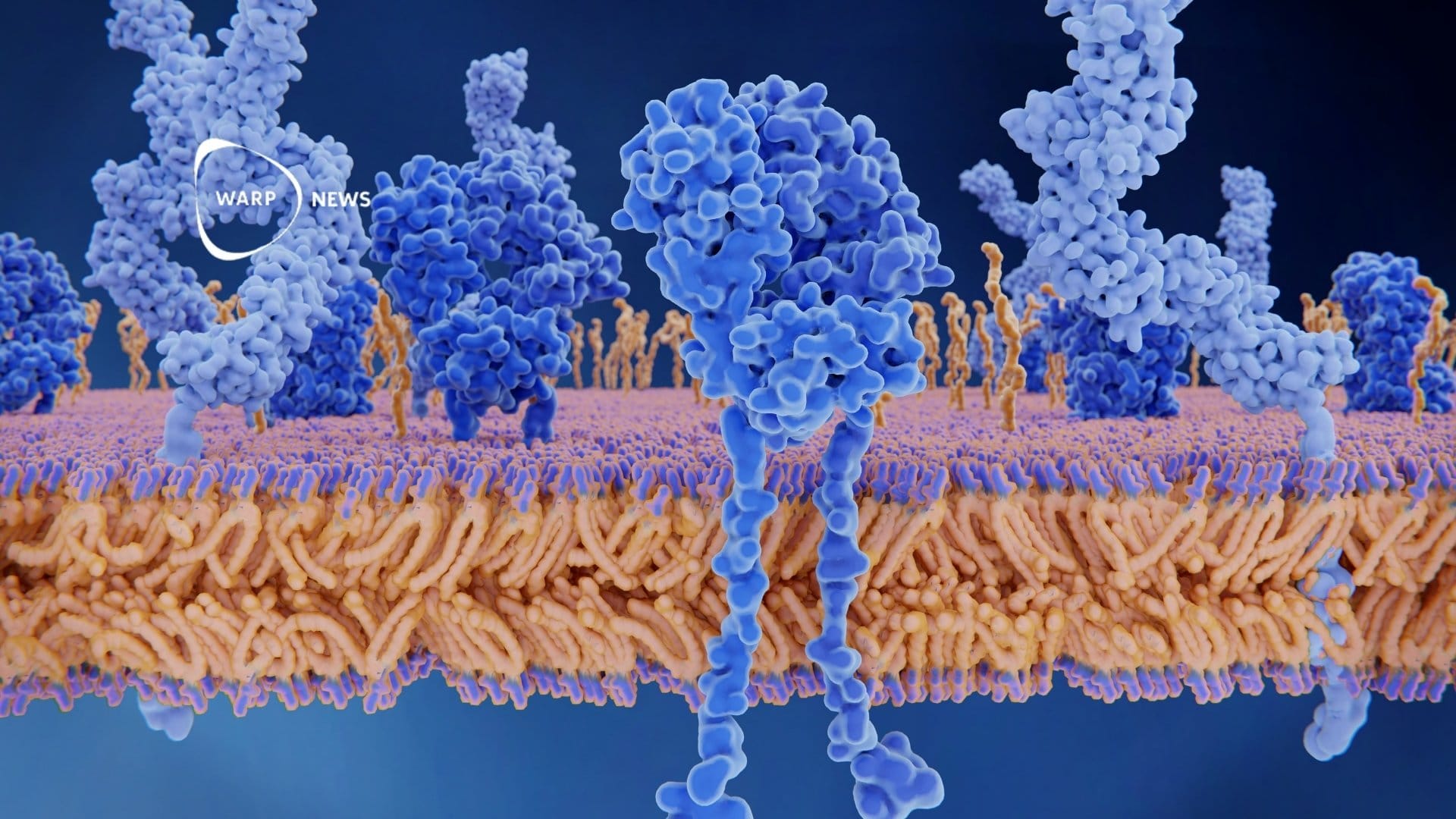
🧪 AlphaFold's protein database has been used by three million researchers in five years
AlphaFold has been cited in more than 35,000 scientific articles. Over 200,000 articles have used elements of AlphaFold 2 in their methodology. It has contributed to understanding heart disease, conserving bee colonies, and developing more resilient crops.
🦾 AI tool analyzes startups 537 times faster than human analysts
AI agents can screen early-stage startups 537 times faster than human venture capital analysts without sacrificing quality. The AI tool cost an average of 6.9 cents per search compared to 70 dollars for human analysis. Startups selected by the AI agent had a higher probability of receiving funding.
✍️ New AI enables people without CAD training to create 3D models from hand sketches
The AI transforms a hand-drawn sketch into a complete, CAD-ready 3D model, can iterate and improve the design based on visual cues and engineering rules, and enables people without CAD skills to create professional-quality models.
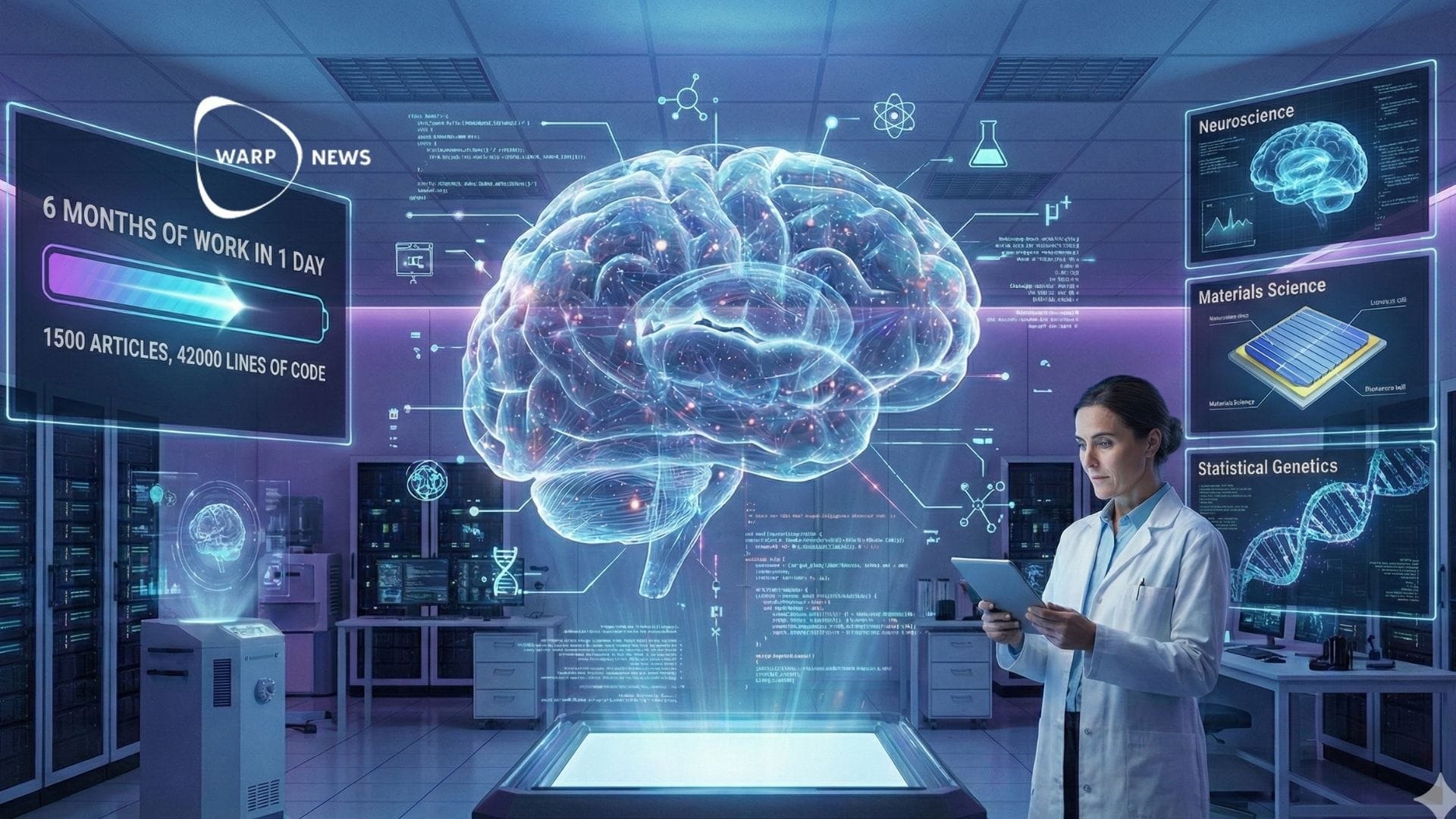
🦾 AI scientist performs six months of work in one day
Kosmos can read 1,500 scientific papers and run 42,000 lines of analysis code in a single run. The AI system has already made seven discoveries in neuroscience, materials science, and statistical genetics.
🦾 New AI-designed enzyme breaks down plastic foam into recyclable building blocks
An AI-designed enzyme can break down 98 percent of polyurethane in 12 hours at industrial scale. Polyurethane is a type of plastic used in foam cushions, mattresses, insulation and other products. The process recovers pure building blocks that can be used to manufacture new plastic.
🧠 Conversation-based dementia therapy – a problem only generative AI can solve
Three years ago, not even one of the largest companies in the world could solve this problem. Now a small startup can. The reason is generative AI.
📗 Book excerpt: A steam engine for the brain
An excerpt from The Fifth Acceleration: Why AI Is Not the End – but the Beginning of What We Can Become by Mathias Sundin.