Child deaths
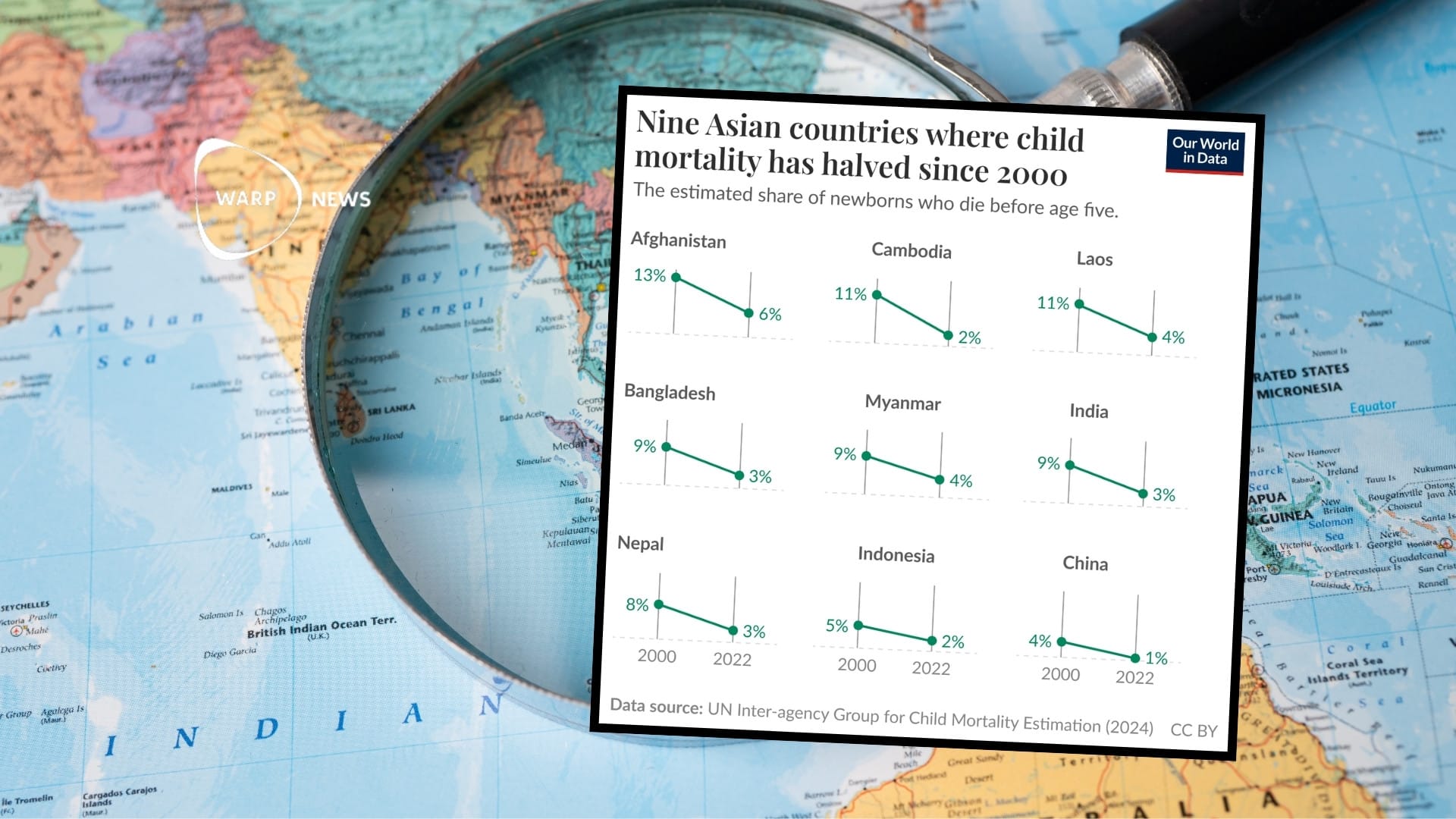
🧒 Child mortality halved in these nine Asian countries
Afghanistan shows the largest decline from 13 percent to 6 percent, while China now has the lowest level at only 1 percent. Improvements in nutrition, clean water, sanitation, vaccinations, and poverty reduction have contributed to this positive development.
👶 Sharp global decline in neonatal tetanus
The number of reported cases of neonatal tetanus has decreased by 89 percent between 2000 and 2021. 47 of 59 priority countries have achieved WHO's goals to eliminate tetanus in mothers and newborns.
🧒🏿 UN: Historic milestone as the number of child deaths falls below 5 million for the first time
Since 2000, the global under-five mortality rate has more than halved. Several low- and lower-middle-income countries have surpassed the global decline, with some reducing child mortality by more than two-thirds.