❤️ Health Tech
Health Tech, or digital health, helps us understand and take control of our own health. But we also cover more traditional health news like medicines, vaccines and medical procedures.
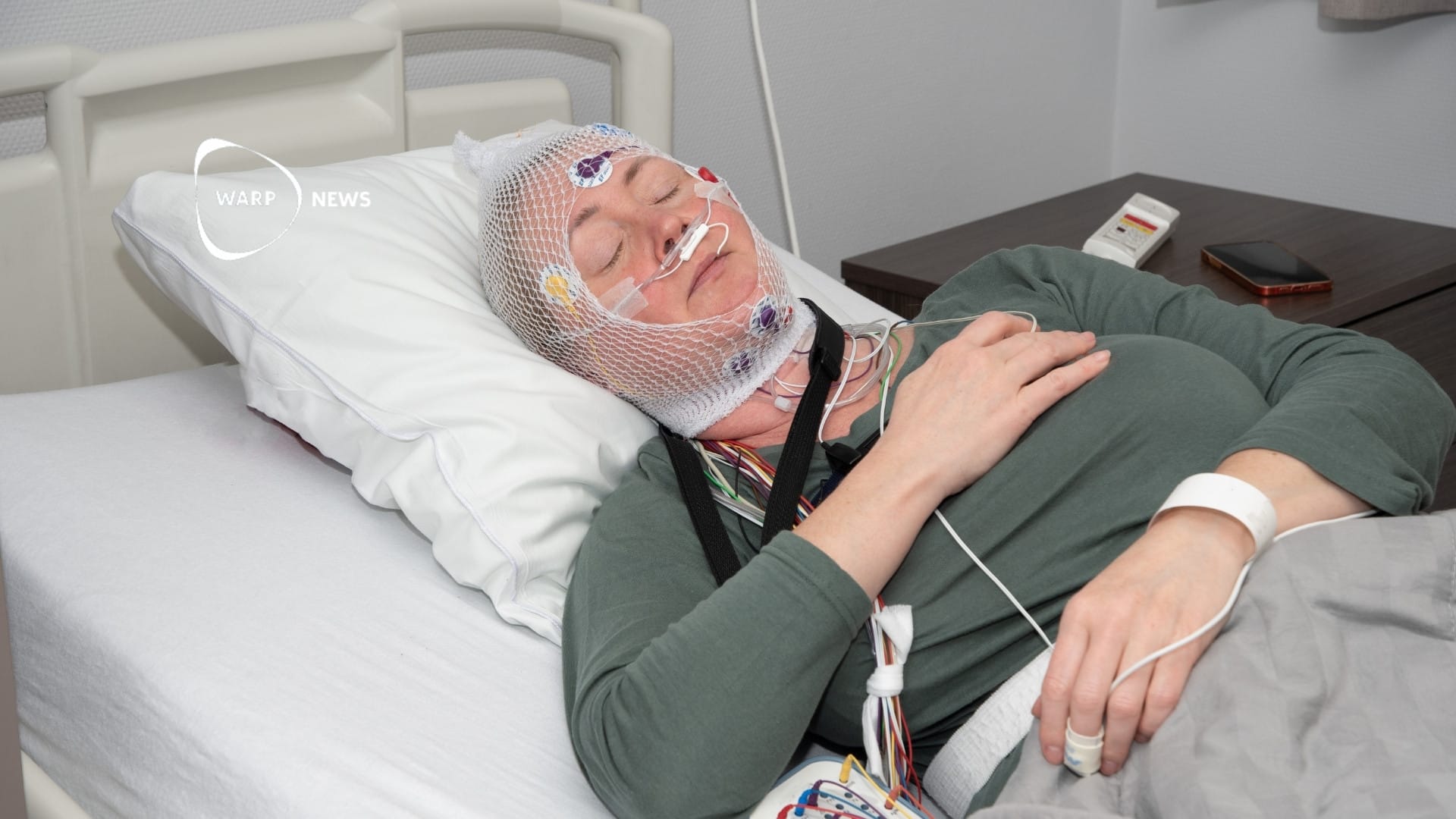
😴 New AI model can predict over 100 diseases from one night's sleep
The model was trained on nearly 600,000 hours of sleep data from 65,000 participants and shows high accuracy for cancer, heart disease, and dementia, among others. The AI model performs as well as or better than today's leading methods for sleep analysis.
👩⚕️ Huntington's disease has been successfully treated for the first time
A gene therapy has for the first time been shown to slow Huntington's disease by 75 percent after three years in a clinical trial. The results provide proof that the disease can be treated, opening possibilities for other neurodegenerative conditions as well.
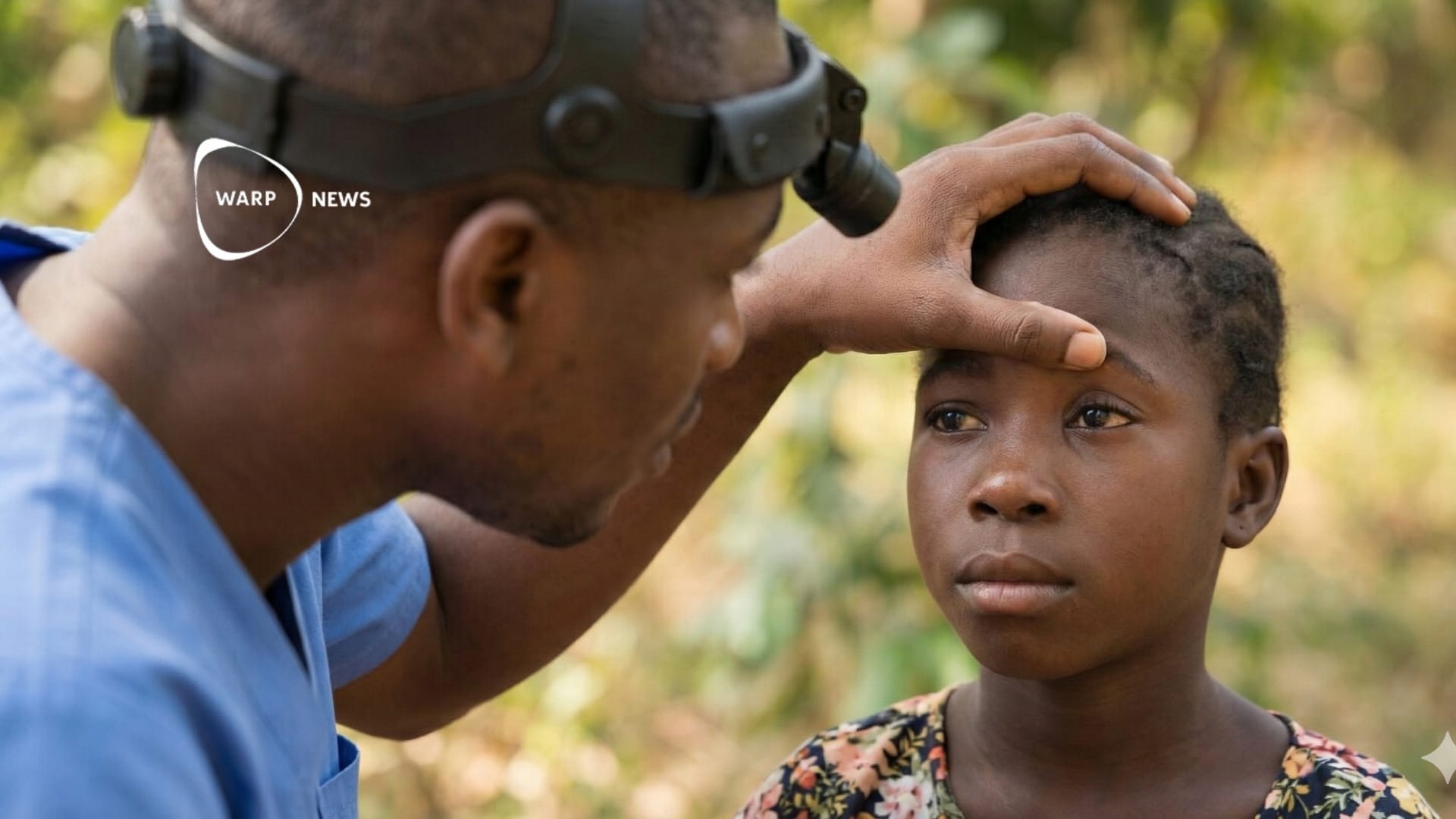
👁️ Number of people needing treatment for trachoma has decreased by 94 percent
Trachoma is the world's leading infectious cause of blindness. The number of people requiring interventions against trachoma has dropped from 1.5 billion to 97.1 million since 2002. Over 1.1 billion doses of antibiotics have been donated to combat the disease.
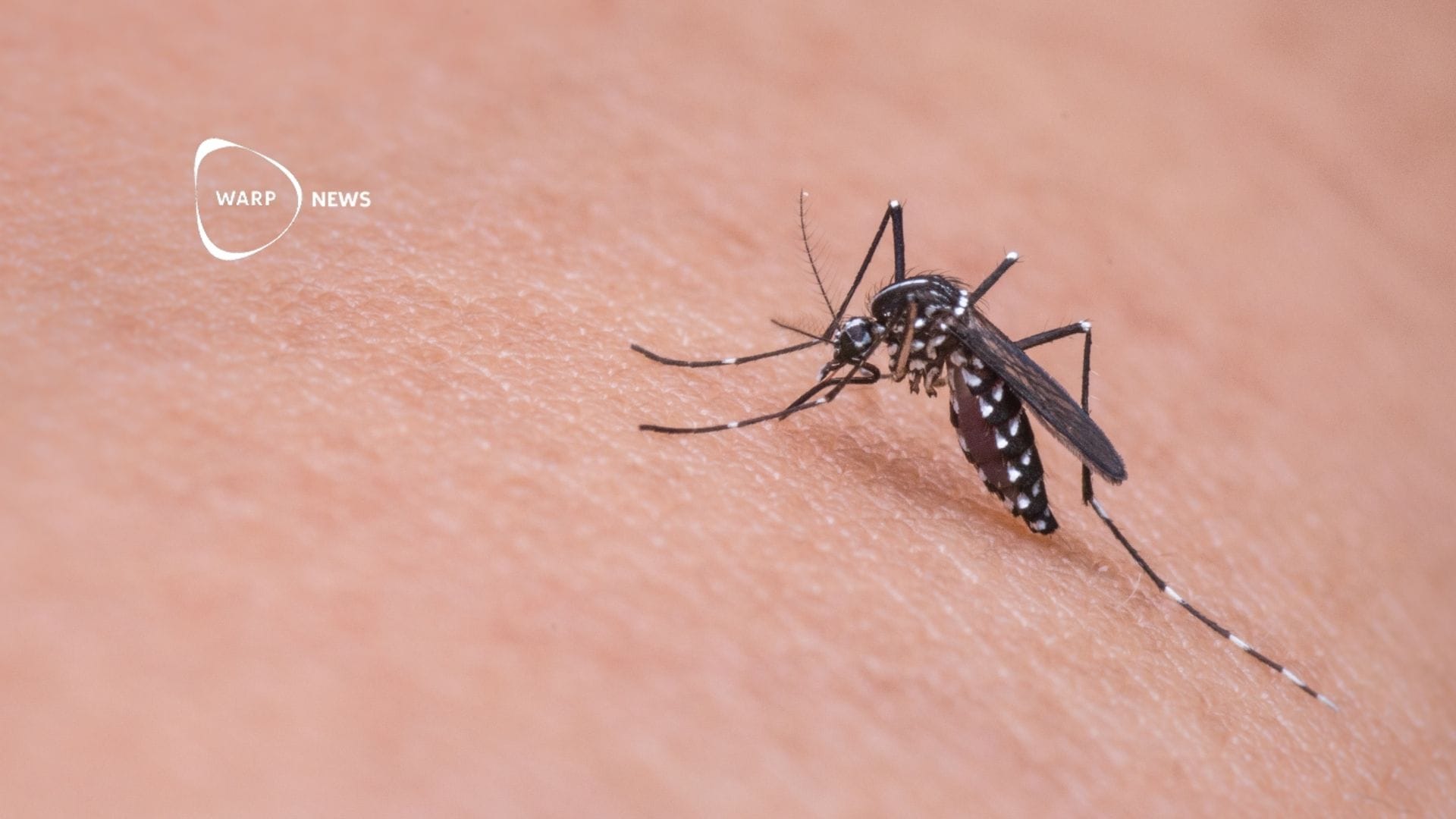
🦟 Scientists succeed in creating mosquitoes that block malaria
Researchers in Tanzania have for the first time in Africa created genetically modified mosquitoes that prevent the malaria parasite from developing. The modified mosquitoes contain naturally occurring molecules from frogs and bees that effectively stop the parasite Plasmodium falciparum.
🎗️ New method creates cancer-fighting immune cells directly in the body – clinical trials show promising results
All eight patients with multiple myeloma in two clinical trials had their cancer cells eliminated from the bone marrow. The method could make CAR-T treatment faster and cheaper. Several pharmaceutical companies are now investing in the technology, and more clinical trials are underway.
🤰 New obesity drug delivers highest weight loss yet in clinical trial
Patients on the highest dose lost an average of 23.7 percent of their body weight after 68 weeks. The drug also reduced knee arthritis pain by up to 62.6 percent. More than one in eight patients who took the drug became completely free of knee pain by the end of the trial.
💩 Goodbye, camera up the bum – swallowable bacterial capsule can detect intestinal diseases
Researchers have developed a capsule with bacteria that is swallowed, detects bleeding in the gut, and can then be easily collected from stool using a magnet. The entire process from collection to analysis takes about 25 minutes.
💉 New vaccine can stop meningitis in Africa
A five-in-one vaccine has begun to be used in several African countries to protect against bacterial meningitis. The vaccine costs only three dollars per dose and protects against four types of bacteria that cause almost all meningitis epidemics in the region.
🩸 Promising: Blood test can detect more than 50 cancer types – enables earlier treatment
A blood test shows ability to identify over 50 different cancer types and can speed up diagnosis. More than half of the cancer forms were detected in early stages where treatment is more effective. Three-quarters of the detected cancer types currently lack screening programs.