💡 Innovation
🛫 Airplane contrails warm the climate less than scientists thought
New research shows that contrails from airplanes cause warming equivalent to two-thirds of the carbon dioxide emissions from jet fuel, not three times as much as previous studies indicated. Airlines are now conducting trials to avoid creating climate-affecting contrails.
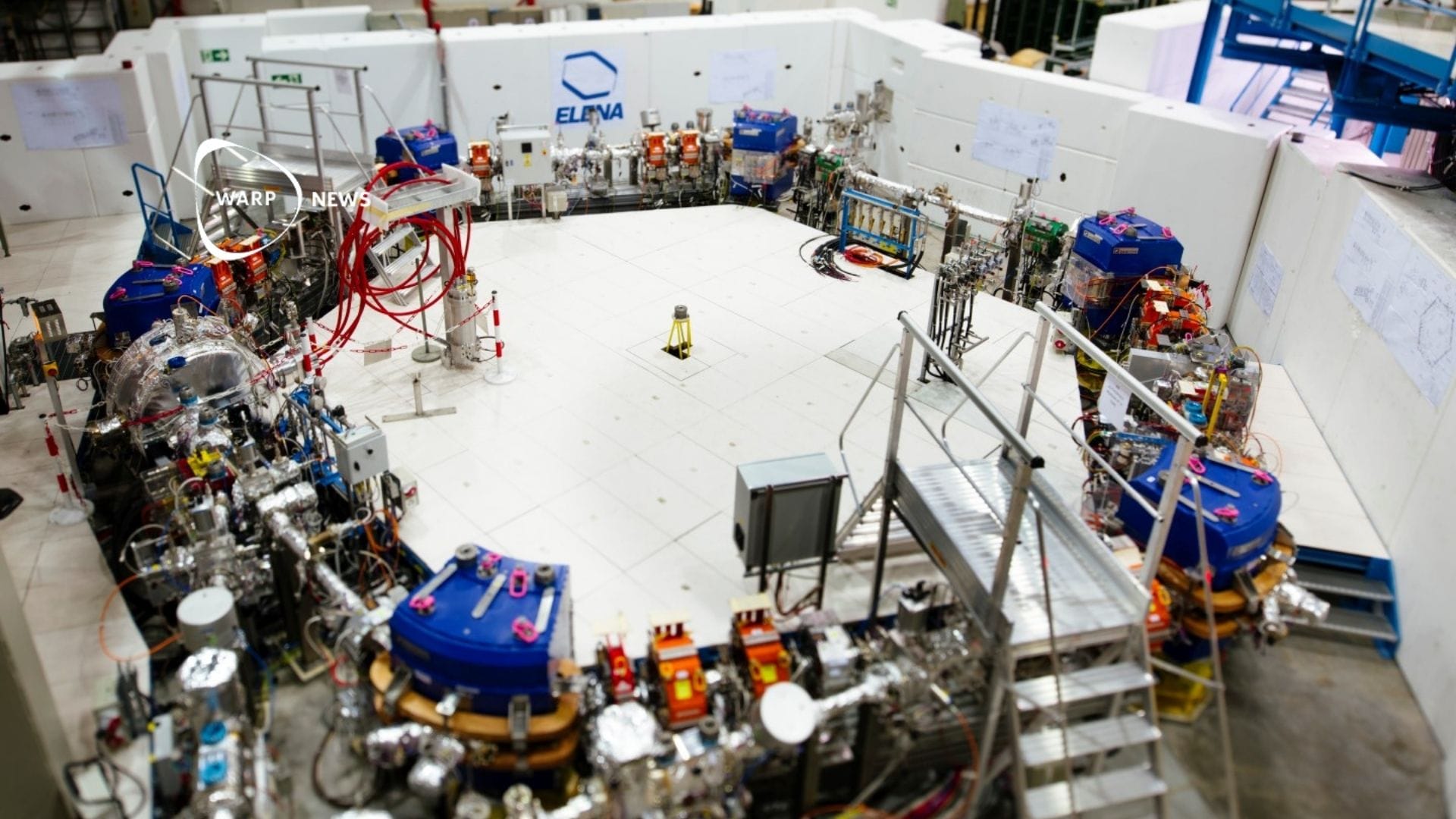
⚛️ New cooling technique increases antimatter production eightfold at CERN
CERN can now produce over 15,000 antihydrogen atoms in under seven hours, compared to ten weeks previously for similar quantities. With larger quantities of antihydrogen available, researchers can now investigate atomic antimatter in greater detail and at a faster pace than before.
🌾 Scientists use CRISPR to create wheat that produces its own fertilizer
The modified wheat produced higher yields under low fertilizer levels compared to regular wheat. For many developing regions, this development could offer new support for reliable crop production.
🐭 Researchers simulate entire mouse brain with nine million neurons
The supercomputer Fugaku has created one of the world's largest and most detailed simulations of a brain, with nine million neurons and 26 billion synapses from the entire mouse cortex. The simulation can be used to study diseases like Alzheimer's and epilepsy in a virtual environment.
🧬 Scientists have for the first time sequenced RNA from 40,000-year-old mammoth
The RNA shows which genes were active in the muscles just before the mammoth died, providing direct evidence of gene regulation in real time. The results show that RNA can survive much longer than previously thought, opening up the possibility of studying RNA viruses from the Ice Age.
🦾 New AI-designed enzyme breaks down plastic foam into recyclable building blocks
An AI-designed enzyme can break down 98 percent of polyurethane in 12 hours at industrial scale. Polyurethane is a type of plastic used in foam cushions, mattresses, insulation and other products. The process recovers pure building blocks that can be used to manufacture new plastic.
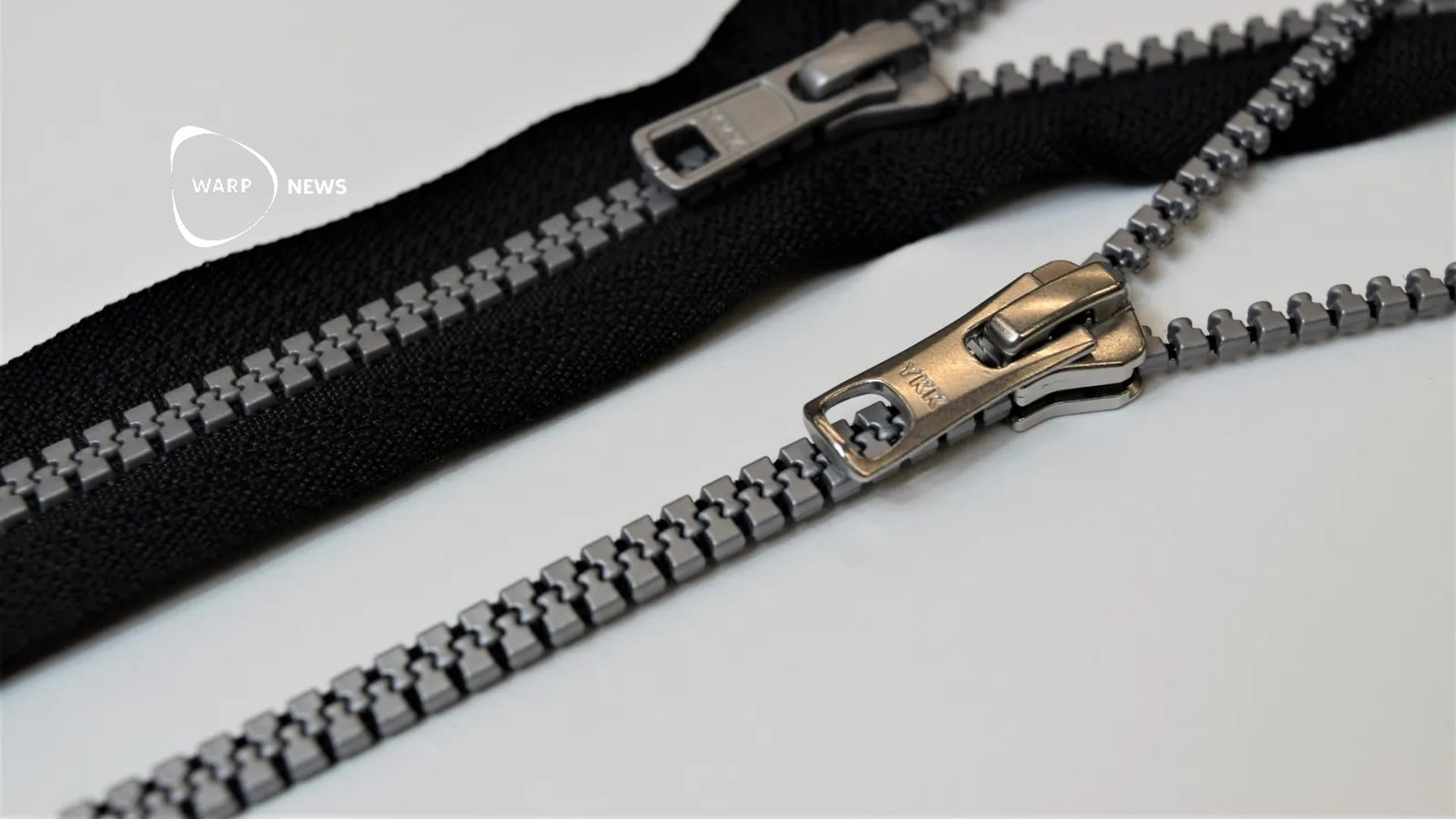
🤐 After a hundred years: New zipper that is more flexible and reduces emissions
YKK has developed a zipper without the woven fabric that normally sits on the sides of the teeth. The new zipper weighs less, is more flexible and reduces both material use and emissions. The North Face and other clothing companies have started using the new technology in their products.
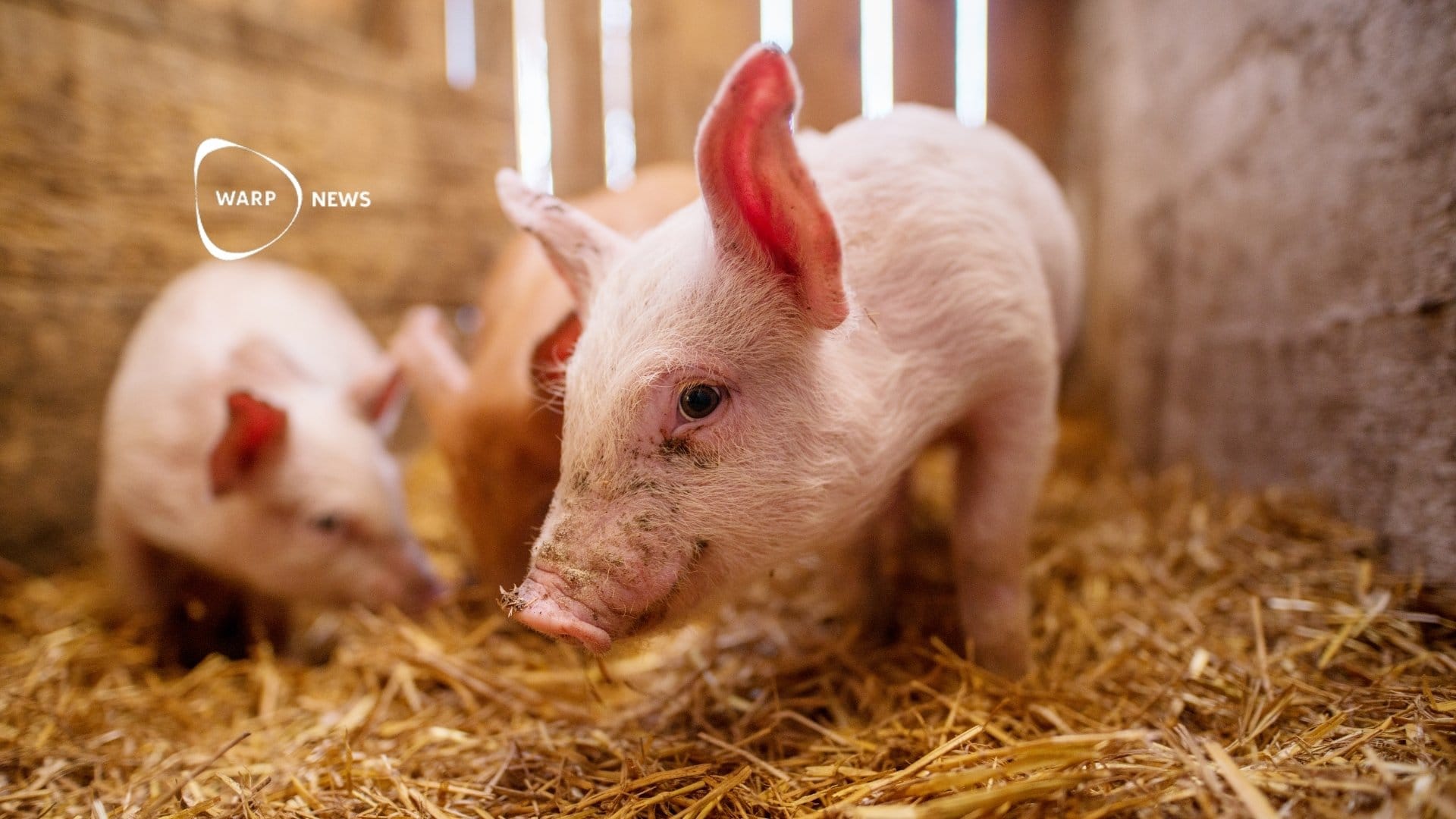
🐖 Gene-edited pigs resistant to classical swine fever
Gene-edited pigs remained healthy when exposed to the deadly classical swine fever virus. The same gene editing may provide resistance to similar viruses that infect cattle and sheep.
🖥️ Quantum computer demonstrates controlled advantage over supercomputer for the first time
The Willow chip calculates molecular structures 13,000 times faster than one of the world's fastest supercomputers. The technique can be used to measure distances in molecules and provide more information about chemical structure than today's methods.