💊 Cure for MS-like disease
Immunotherapy, inspired by revolutionary cancer treatment, eliminates disease-causing cells in MS-like disease.
Share this story!
The immunotherapy CAR-T revolutionized cancer care when it was introduced in 2017. Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, have now used the same method to treat mice with an autoimmune disease similar to MS, the university announced on its website.
“We succeeded in using CAR-T cells to eliminate the cells that caused the autoimmunity but not other immune cells needed to protect against viruses or other infections. Our CAR-T cells were very effective in treating mice that had MS-like disease.” said Chyi-Song Hsieh, one of the lead authors of the study.
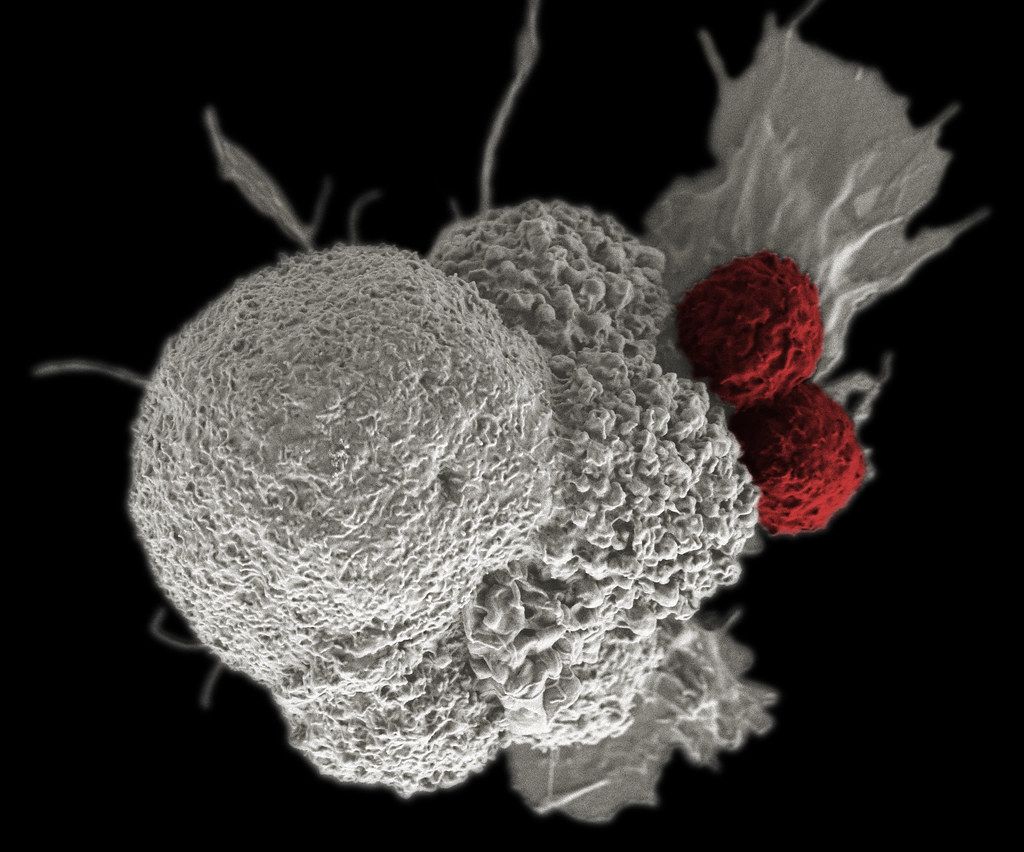
CAR-T treatment for cancer works, somewhat simplified, by reprogramming the patient's white blood cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. Since an autoimmune disease like MS means that a person's immune system plays tricks and attacks the body's healthy cells, the researchers took inspiration from the CAR-T treatment and tried to adapt it to recognize and attack the blood cells that act in that way.
By combining part of a protein found in myelin with a protein that activates T cells (the adaptive part of the body's immune system), they created a trap that only the white blood cells that aren't working as they should attack. When the trap was then set on so-called killer T cells, the result was that the white blood cells that went after the molecule were themselves eliminated.
When the method was used on mice with an MS-like disease, it was found to work well. Mice that already had symptoms had reduced signs of disease, while mice that had not yet developed symptoms remained symptom-free.
The research group is now working on improving the method so that it becomes more efficient and maintains its function for a longer period. According to the research team, this approach looks very promising for eventually curing MS.
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.