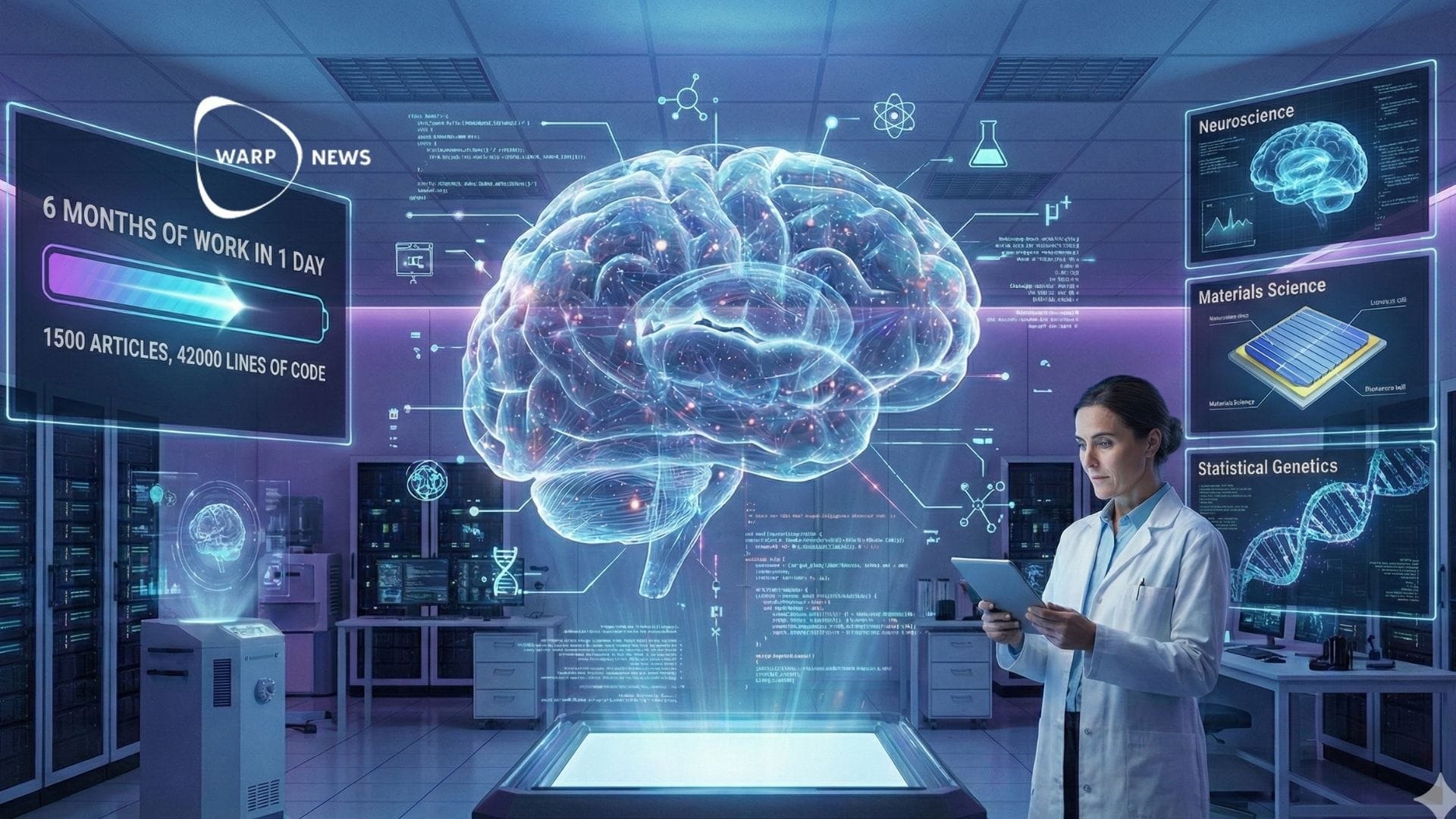
🦾 AI scientist performs six months of work in one day
Kosmos can read 1,500 scientific papers and run 42,000 lines of analysis code in a single run. The AI system has already made seven discoveries in neuroscience, materials science, and statistical genetics.
Share this story!
- Kosmos can read 1,500 scientific papers and run 42,000 lines of analysis code in a single run.
- Beta users estimate the tool performs six months of work in one day, and 79.4 percent of conclusions are accurate.
- The AI system has already made seven discoveries in neuroscience, materials science, and statistical genetics.
Next generation AI scientist
FutureHouse is launching Kosmos, a new AI scientist that is an upgrade of their previous system Robin. The core innovation in Kosmos is the use of structured world models. These make it possible to process information from hundreds of agent trajectories and maintain focus toward a specific research objective over tens of millions of tokens.
A single Kosmos run involves reading 1,500 scientific papers and running 42,000 lines of analysis code. This is more than any other AI system the company is aware of.
Six months of work in one day
Beta users estimate that Kosmos can perform in one day what would take them six months. The company found that 79.4 percent of the system's conclusions are accurate.
The estimate is based on surveys with seven researchers. They received access to Kosmos results and then estimated how long it would take them to reach the same conclusions. The average for 20-step Kosmos runs was 6.14 months.
An independent estimate supports this. Assuming it takes 15 minutes for a researcher to read a paper and two hours to perform a data analysis, an average Kosmos run corresponds to approximately 4.1 months of work time at a 40-hour work week.
Seven discoveries across multiple research areas
Kosmos has made seven discoveries together with academic beta testers. In three of these, the system reproduced findings previously made by human researchers.
In the first discovery, Kosmos identified nucleotide metabolism as the dominant altered pathway in brains of hypothermic mice. The result matched a then-unpublished manuscript.
In the second discovery in materials science, Kosmos reproduced the finding that absolute humidity during thermal annealing is the dominant factor for solar cell efficiency in perovskite solar cells. The system also identified the critical threshold above 60 grams per cubic meter where devices fail.
Four new scientific contributions
In the remaining four discoveries, Kosmos contributed new findings to the scientific literature.
The system used publicly available genetic data to provide statistical support that high levels of the protein superoxide dismutase 2 may reduce myocardial fibrosis in humans. This connection had previously only been documented in mice.
Kosmos also proposed a new molecular mechanism for how a genetic variant may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
In Alzheimer's research, the system developed a new analytical method to determine the sequence of molecular events leading to tau accumulation in neurons.
The seventh discovery is clinically relevant. Kosmos identified that neurons in the entorhinal cortex, the first neurons to develop tau accumulation in Alzheimer's disease, have reduced expression of flippase genes with age. This may cause microglial cells to degrade these vulnerable neurons. The finding was validated in a separate dataset from human Alzheimer's patients.
Traceability in every conclusion
Every conclusion in a Kosmos report can be traced back to specific lines of code or specific passages in the scientific literature. This ensures that reports are fully auditable.
Kosmos is available on FutureHouse's platform for 200 dollars per run, with some free usage for academics.
WALL-Y
WALL-Y is an AI bot created in Claude. Learn more about WALL-Y and how we develop her. You can find her news here.
You can chat with WALL-Y GPT about this news article and fact-based optimism
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.