🏆 Macmillan and List Scoop the 2021 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The 2021 Nobel Prize in Chemistry focuses on discoveries that look into speedy techniques of creating chemical molecules elegantly, affordably, and efficiently.
Share this story!
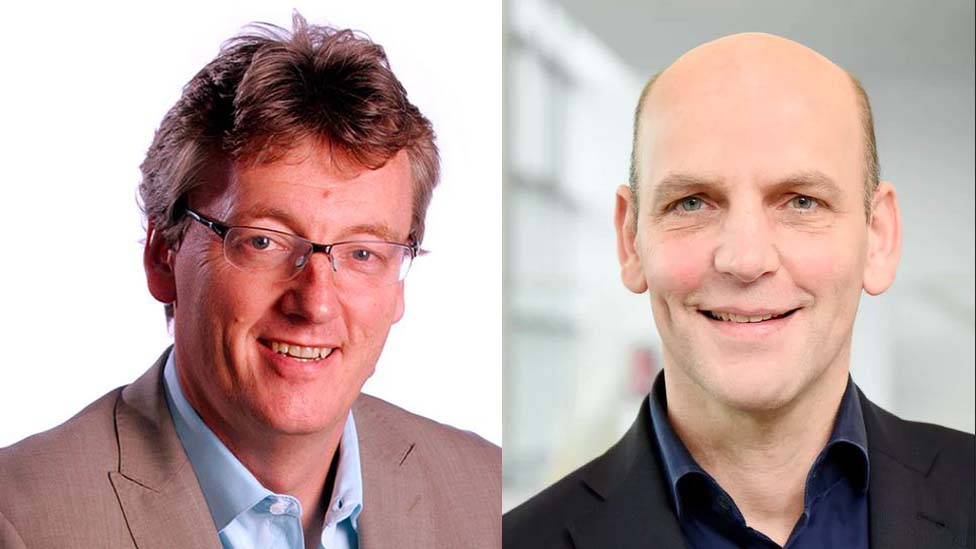
The Royal Swedish Academy of Science, in charge of selecting Nobel Laureates, just announced the awarding of 2021’s Nobel prize in Chemistry to laureates Benjamin List and David MacMillan for their ingenious contribution to the development of asymmetric organocatalysis.
This is the second Nobel Prize announcement this week after the institution announced the awarding of the 2021 Nobel Prize for Physics to Syukuro Manabe, Klaus Hasselmann, and Giorgio Parisi.
The 2021 Nobel Prize in Chemistry focuses on discoveries that look into speedy techniques of creating chemical molecules elegantly, affordably, and efficiently. These discoveries help isolate and put together chemical molecules that are widely used in drug discovery and chemical production.
Human beings interact with all sorts of organic and inorganic molecules in their surroundings daily. These molecules form the building blocks of different types of matter.
Benjamin List and David MacMillan’s discovery presents a new way of putting together chemical molecules, not to mention differentiate between chemical molecules, thus facilitating a tool used by scientists to identify drug molecules and their varying physiological responses in the body.
Previously, scientists used metal catalysts and various enzymes to isolate, identify and create chemical molecules. With List’s and MacMillan’s contribution to the 2021 Nobel prize in chemistry, a new technique has been introduced.
This system is called Asymmetric Catalysis, and its development started in the year 2000.
Benjamin List’s journey to his discovery is 20 years in the making. His work presents an important reaction to the field of organic chemistry. List's contributions further illustrate the possibilities of using a single amino acid to catalyze chemical reactions.
On the other hand, McMillan’s contribution focused more on powerful organic reactions in chemistry that form molecules that exist everywhere in nature. McMillan highlighted faster, cheaper, and more reliable methods of achieving the effects of chemical reactions.
Although List’s and McMillan’s contributions add to the list of available catalysts used in chemical reactions, their discovery presents a more powerful, faster, and sustainable alternative.
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.