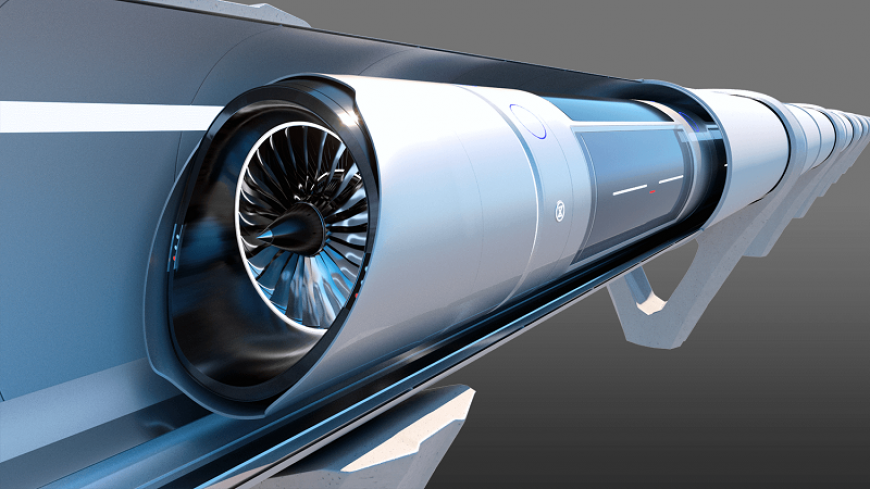
🚄 Hyperloop – the future of superfast and sustainable travel
The future of screaming fast and environmentally friendly transportation is under construction. Get comfy and take a seat as Warp News writer Vincent Roose takes you on a ride with Hyperloop.
Share this story!
Summary
📉 What people think
When considering the Hyperloop, it is a mistake to focus only on the current financial aspect. Yes, as for today, the Hyperloop and its development are costly. However, there are other elements to consider: it is a green, responsible, smart, and efficient mobility option for the future.
And with time will come improvements that will reduce the costs and improve the financial perspective of the Hyperloop.
📈 Here are the facts
A detailed analysis of the Hyperloop potential revealed important insights compared to other transports – high-speed trains and airplanes.
In terms of operational performance, the Hyperloop should provide a high-quality service, however, tempered by its relatively low capacity of 14 passengers per vehicle.
This aspect impacts the next performance axis analyzed: the financial performance. In this regard, the Hyperloop still has higher costs because it requires its own operating ground.
But the Hyperloop not only shows real strength in terms of social and environmental performance. Indeed, thanks to its engineering, it needs less energy to travel at supersonic speed and cover long distances. It should cause no noise pollution and suffer fewer damages.
💡 Optimist's Edge
Despite its relatively high current cost, the Hyperloop appears like a great solution to replace airplane transports without extending travel time. And this strength has been recognized by European institutions.
It would be a quality service, a green way to travel over long distances, and bring the risks of incidents down as close as possible to zero. In addition, it is essential to find alternatives to polluting transportations.
It can also be a complement to regular trains to create a highly effective railway network.
👇 How to get the Optimist's Edge
To get the edge, there is still work to be done on making the Hyperloop more cost-effective and attractive. The main possibility is to improve the capacity of each vehicle without impacting the safety standards. Only through research, which you can support, could that be possible.
Another option is to support companies that are developing the Hyperloop. As for 2021, HyperloopTT and Virgin Hyperloop are the two leading companies planning on ten projects across the world. Investing and supporting them and increasing their resources should help turn the future into reality earlier.
📉 What people think
The danger is to consider the Hyperloop technology only from the perspective of its expected financial performance and cost at the moment.
But focusing only on this aspect is a short-term perspective and ignores the strengths the Hyperloop has over other transportation options of the same category.
It will take time to reduce the cost and price. Still, the benefits for the environment, neighborhoods, travel time, and safety are undeniable and must be taken into account when considering the projects.
📈 Here are the facts
To take the words from the Spanish Hyperloop company Zeleros:
"Hyperloop is the world's fastest land transport system for fully electric and automated intercity travel. Hyperloop capsules move levitating at high speeds inside a network of low-pressure tubes."
The concept of the Hyperloop emerged in the 2010s to solve two issues. First, the air routes are overcrowded with planes that release significant amounts of greenhouse gases. Second, regular trains are, as of today, too slow to cover long distances.
Thus, arose the idea to push one existing technology – the magnetic levitation – to its full potential. So, how does that work, really?
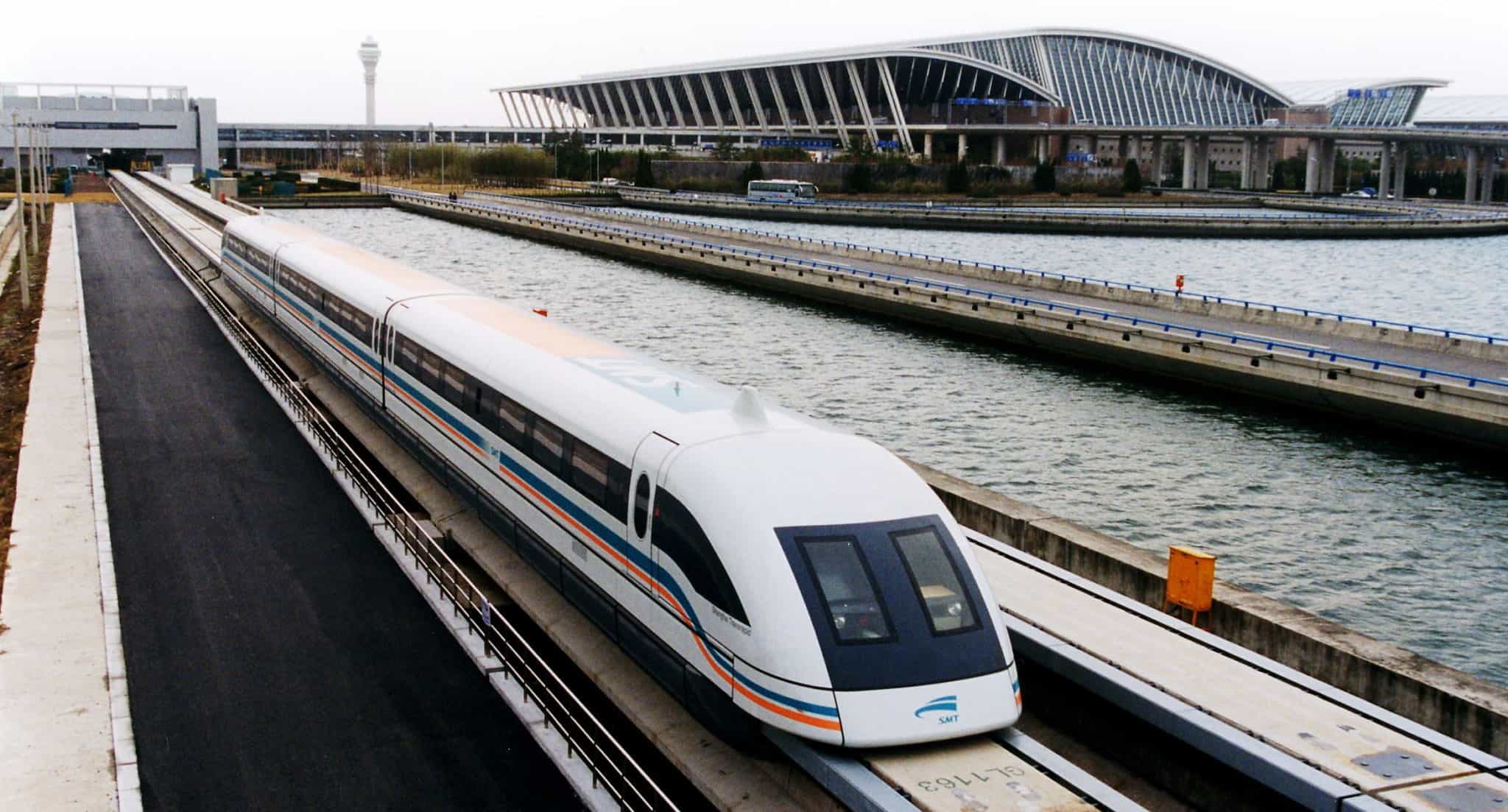

With two sets of magnets, it is possible to generate movement and use the lack of friction that wheels would cause to maintain a very high speed with a relatively small impulse. First developed in the 1940s in England, maglev trains are used in countries like Japan, South Korea, Germany, and China.
But despite real advantages, maglev trains have failed in becoming a dominant means of transportation.
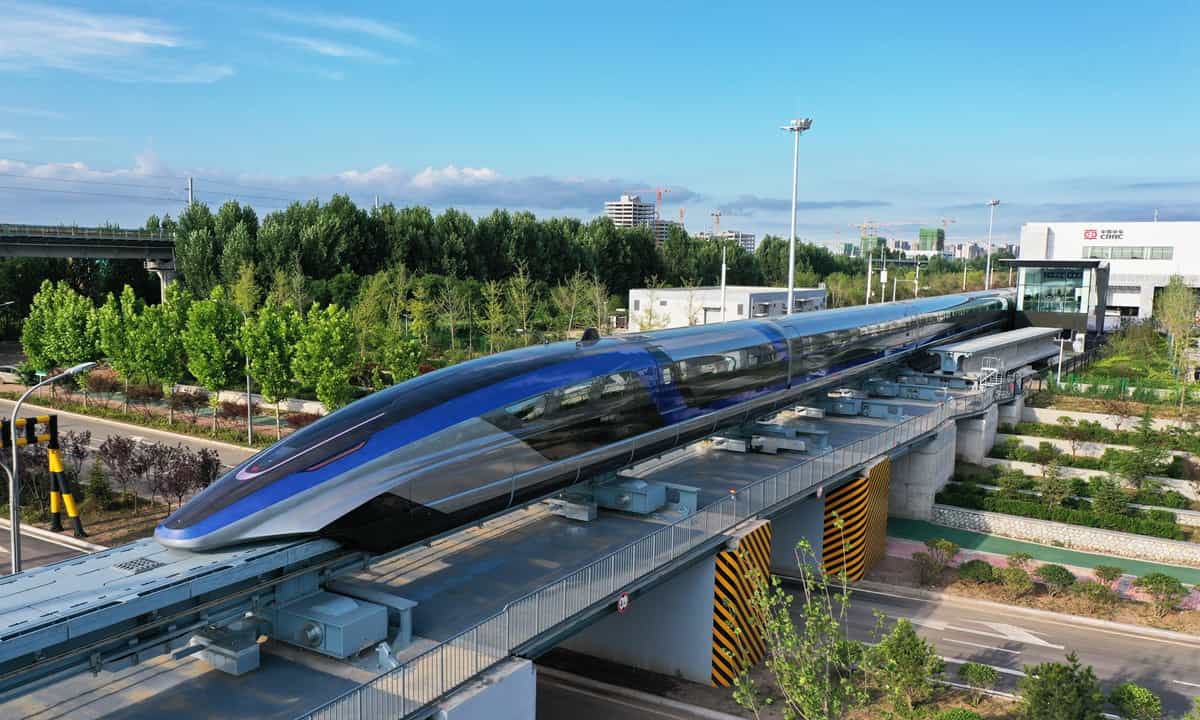

Elon Musk's project – Hyperloop
The novelty of Elon Musk's project, hyperloop, is to place the vehicle in a tube to avoid all friction with the air. The speed potential increases significantly, reaching the supersonic range. Interestingly, this idea is, in fact, not so new.
As explained by the historian of technologies R.A Buchanan, this concept of the underground and atmospheric railway can be traced back as early as 1799! But Elon Musk is granting it the breath to exist.
In an article published in 2018, van Goeverden et al. analyzed the features of the Hyperloop in comparison with regular High-Speed Train and Air transportation. Its performances were scrutinized based on three aspects. The operational performance, the financial performance, and the social/environmental performance.
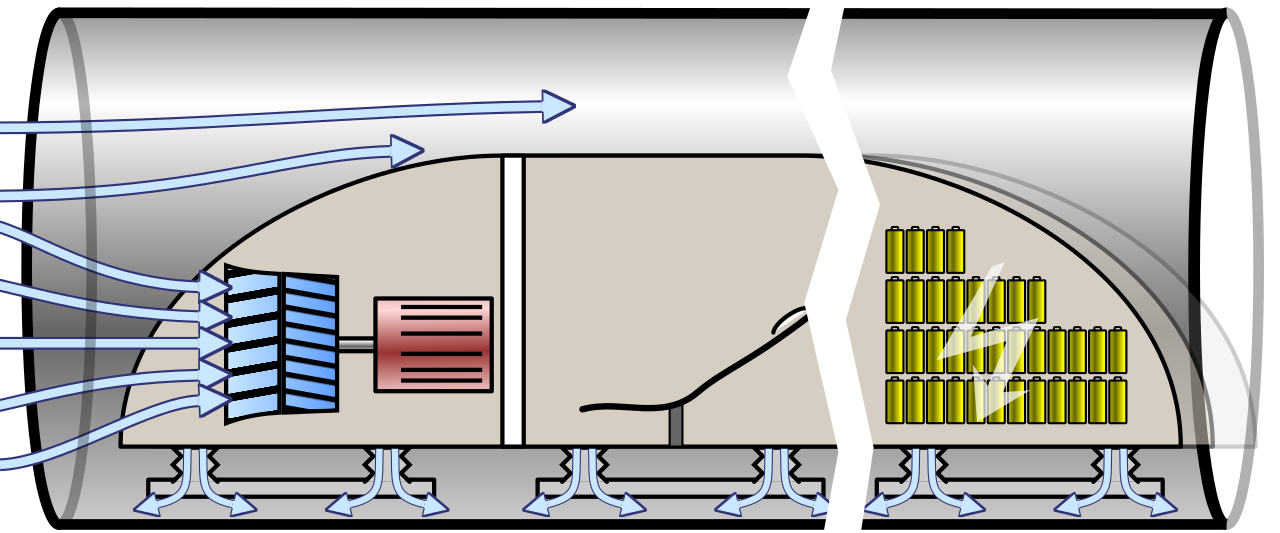
Operational performance
This set of performances focuses on the capacity and quality of the service. And this aspect of the hyperloop displays both strengths and weaknesses. Indeed, its capacity as for now is low compared to that of trains. However, as van Goeverden et al. acknowledged, the Hyperloop could bring people straight into the heart of cities. Something planes can't easily do. Then, thanks to its high level of automation, it would bring down the risks of suffering from reliability issues. And the closed environment would also reduce factors of degradation due to weather.
Financial performance
Financial performance is one of the weaknesses of the hyperloop project. Just like the maglev trains, or regular trains, the hyperloop requires a specific infrastructure and network. The construction of the vehicles, maintenance of both the tubes and vehicles, and operational costs add to the list of expenses. And as evoked, the capacity is relatively low, which does not help in terms of financial performance, especially in comparison to trains and air transports.
That cost issue is sometimes regarded as the reason for the unpopularity of maglev trains around the world. And critics have raised concerns regarding estimations made by Elon Musk.

Social and environmental performance
According to Goeverden et al., this is the best asset of the Hyperloop. Firstly, thanks to its physical and technical properties, it requires a smaller amount of energy to cover much longer distances compared to high-speed trains and airplanes. In addition, the Hyperloop stands as a plausible carbon emission-free solution for mobility.
They furthermore insisted on the likelihood of reduced noise pollution; the Hyperloop operating in its own facility and underground should not produce noise disturbance for citizens.
They eventually evaluated the safety risks and highlighted the minimal risks of damage caused by external interactions. In other words, because the Hyperloop has its own ground, isolated from the outside, the chances of hitting animals, of rain or weather destroying and disturbing its proper functioning, are getting closer to zero than ever. And the intended automated systems should as well prevent human mistakes from causing accidents. The remaining safety consideration is to think of evacuation plans in case of internal incidents.

💡 Optimist's Edge
To make the Hyperloop an attractive transport system, it is essential to capitalize on its strengths; its good environmental balance and increased safety compared to other transportation methods. Trains are much slower and require more energy, and suit other transportation requirements better. Airports and planes are thirsty in kerosene and noisy. The examples of complaints from nearby residents are endless.
A green means of transport for the future
Overall, the Hyperloop should shorten the travel time, with excellent safety and fewer inconveniences. In effect, passengers or goods would be able to move across long distances in time ridiculously slow compared to nowadays. The time between Paris and Berlin, around 1000 km, is estimated to be an hour!
With a complete network all around Europe, which is the target of the Shift2Rail program, the Hyperloop closes the gaps and opens possibilities for business and housing. Someone living in Germany could easily commute to Spain when in-office presence is essential. The unity over the continent would be positively impacted.
And the European Union has already recognized the benefits of developing the Hyperloop, clearly supporting that it "is a big part of the answer to solving today's mobility problems." It opened the path for funding by European institutions.
In the United States, Hyperloop projects are also set to receive the support of the Senate.
Overall, our societies must reset and rethink many of their systems, and the Hyperloop carries unique, inspiring perspectives.
A means to complete the railway network
Furthermore, there is a need for alternatives to current transports. Of course, the Hyperloop will have its flaws, but climate change is happening. Humanity needs to transform its means of communication and transportation, and for continental long-distance journeys, the prospects of the Hyperloop are promising. It could potentially replace the airplane on many routes.
But if it should compete with aerial transports on the market segment of long-distance journeys, a shift is necessary when opposing the Hyperloop to high-speed trains. Instead of seeing them as competitors, the Hyperloop shall come as a complement to the standard railway. They are not aiming at the same markets. Trains are highly effective in carrying many passengers on short to mid-range distances, whereas Hyperloop can connect long distances better.
And there is more as the key players of the Hyperloop development have decided to cooperate. One of the aspects they have agreed upon is the integration of regular rail systems and new technologies as part of one whole.
According to Virgin Hyperloop, by the end of this decade, the Hyperloop may have become part of the regular transport methods.

👇 How to get the Optimist's Edge
The main issue is to increase the Hyperloop's capacity to advance its attractivity by reducing the costs of travel tickets. As for now, the capacity is expected to be around 14 passengers per vehicle. This limit also exists for safety reasons. Yet with further development, it could be possible to improve the capacity.
Hence, there are two angles of investment possible.
Partnering with Universities to solve engineering issues
According to Jonas Kristiansen Nøland, at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology in Trondheim, Norway, there is a lack of academic proof to support the efficiency of specific propulsion methods, specific designs over others. In his paper, he exposes six areas that require research to optimize the Hyperloop.
- Identifying the optimal ratio between the capsule/tube design and their operational energy consumption.
- Electrifying the infrastructure at a small cost relative to the general investment to avoid additional heavy expenses.
- Identifying the optimal magnetic levitation solution.
- Establishing designs that would resist better edge/effects and impacts.
- Finding heat management solutions.
- Developing de-acceleration solutions that resist high braking forces.
The partnerships between companies or investors and universities are becoming more and more attractive. There are plenty of students, researchers looking for topics to explore and finance. Supporting research with financing (post-) doctoral thesis is a great way to stimulate development.
Supporting the existing companies and projects
Two dominant business actors have elected to focus on the Hyperloop. Around the world, multiple projects have been announced. In November 2020, Virgin Hyperloop successfully performed its first passenger tests and is now planning routes between Helsinki and Stockholm and routes in India. The company HyperloopTT has also signed multiple deals to develop lines, for instance, in Ukraine, France, Mexico, United States.

But besides these two leaders, smaller companies are working on their networks. The Spanish company Zeleros has designed its own capsule and will develop a 3-kilometer test track, the longest to date, nearby Valencia. In the Netherlands, Hardt, which is the heart of the European Hyperloop Center, has been awarded €15,000,000 from the European Commission to develop a route between Amsterdam and Rotterdam. And Swisspod is targeting to connect Geneva and Zürich in just under 20 minutes.
The Hyperloop is on.
You now have an advantage because you have gained this knowledge before most others – what will you do with your Optimist's Edge?
❓ What else can you do?
Feel free to share more ideas with other Premium Supporters in ours. Facebook group
By becoming a premium supporter, you help in the creation and sharing of fact-based optimistic news all over the world.


